DNA Testing

What is Paternity testing?
This DNA is a unique genetic fingerprint that comprises every persons genes and chromosomes. Both parents pass on half of his and her DNA to the baby. This genetic code, or DNA, is a shared mix of only the mother’s and father’s DNA. By collecting and examining a small sample of DNA from everyone involved, a DNA paternity test can confirm or disprove that the man in question is indeed the biological father of a child.
Types of Paternity tests
DNA Paternity Testing
This is the most common type, involving the comparison of DNA samples from the alleged father, child, and mother (if available) to determine biological relatedness.
Non-Invasive Prenatal Paternity Testing (NIPT)
This type of test can determine paternity before a child is born by analyzing fetal DNA present in the mother's blood. It's typically performed after the 8th week of pregnancy.
Postnatal Paternity Testing
This involves testing the DNA of the alleged father and child after the child is born. It's a straightforward process commonly performed using cheek swabs or blood samples.
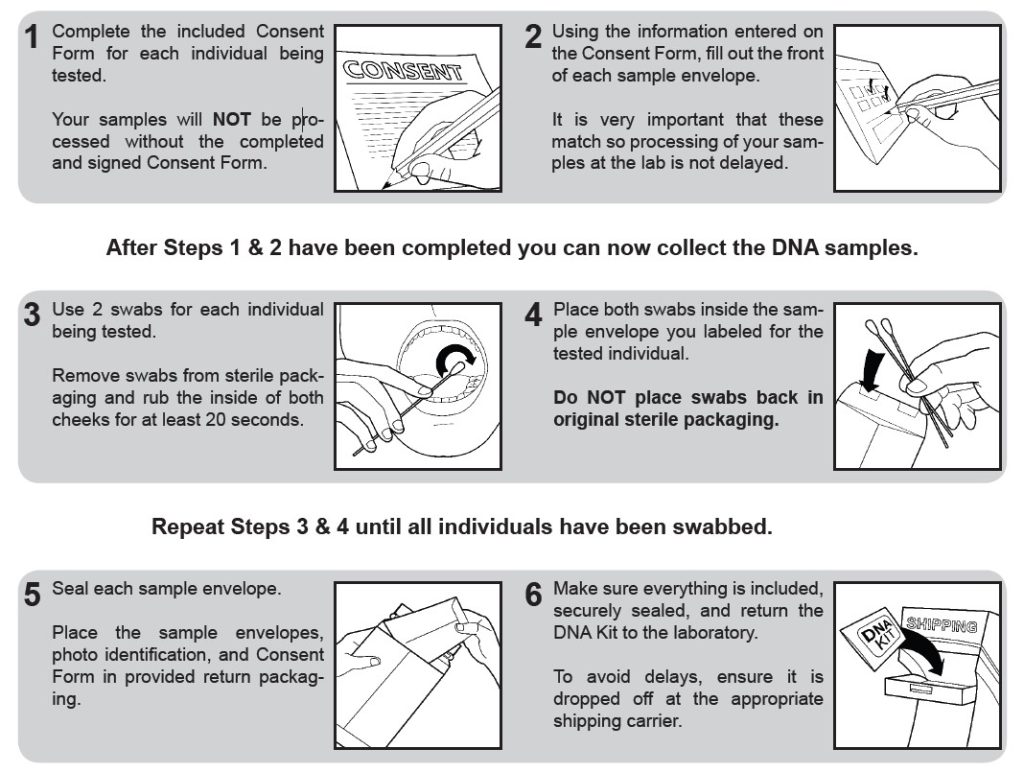
DNA Collection Instructions
Types of DNA Tests
Paternity Testing
Determines biological relatedness between a child and an alleged father.
Maternity Testing
Confirms biological maternity, usually in cases where there's uncertainty about the biological mother.
Ancestry DNA Testing
Traces one's genetic ancestry, providing insights into ethnic origins and genealogical connections.
Genetic Health Testing
Assesses genetic predispositions to certain diseases or conditions, offering insights into potential health risks.
Forensic DNA Testing
Used in criminal investigations to identify suspects or victims, and in other legal contexts.
DNA Profiling/Genetic Fingerprinting
Compares DNA samples for identification purposes, often used in criminal justice and paternity cases.
Whole Genome Sequencing
Analyzes an individual's entire DNA sequence, providing comprehensive genetic information.

